§1. What is SPDT Switch
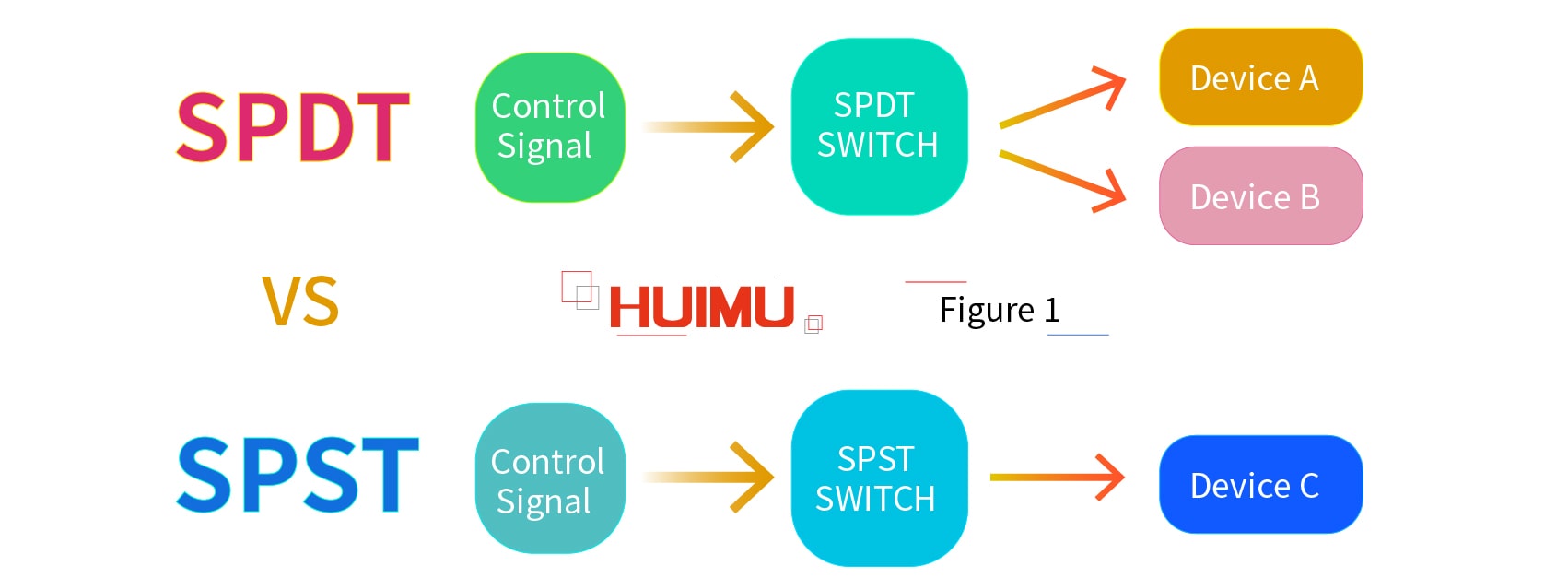
SPDT (Single Pole Double Throw) is a special switch structure. Different with the normal SPST (Single Pole Single Throw) switches, SPDT switches control the working status of two devices, and these two devices work in opposite status. For example, a SPDT switch is connected to Device A and Device B, the Device A will be on status and the Device B is shut down if the SPDT switch is switched off; conversely, if the SPDT switch is switched on, the Device A will be off status and the Device B will be turned on. Therefore, we can know that no matter what state the SPDT switch works on, only one device will be turned on.
1.1 What is the Structure of SPDT Switch
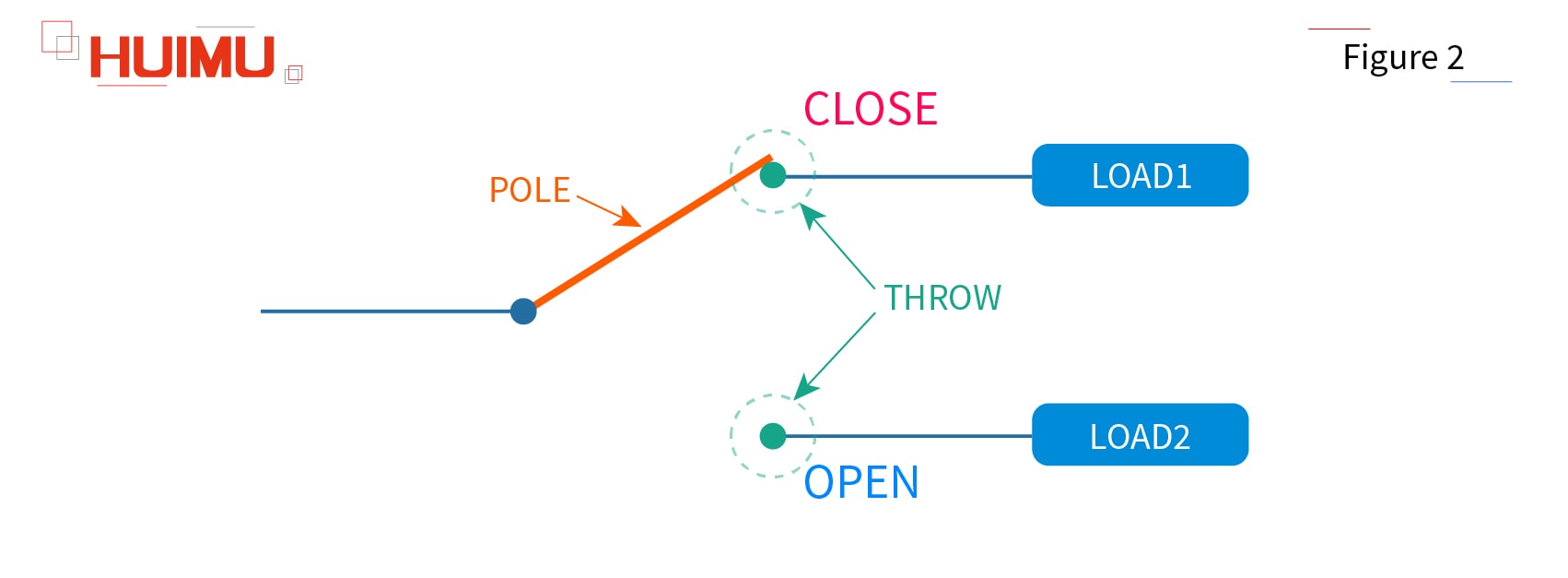
The basics of the SPDT switch structure:
Pole: The pole is the controller inside the switch. We usually use single pole, double pole, or etc. to show how many separate circuits that controlled by the switch.
Throw: The throw means the circuit that will be controlled by the pole. We usually use single throw, double throw, or etc. to show how many circuits will be controlled by one Pole.
Open: If the pole is disconnected to one throw, the state of this throw is called open state or open.
Close: If the pole is connected to one throw, the state of this throw is called close state or close.
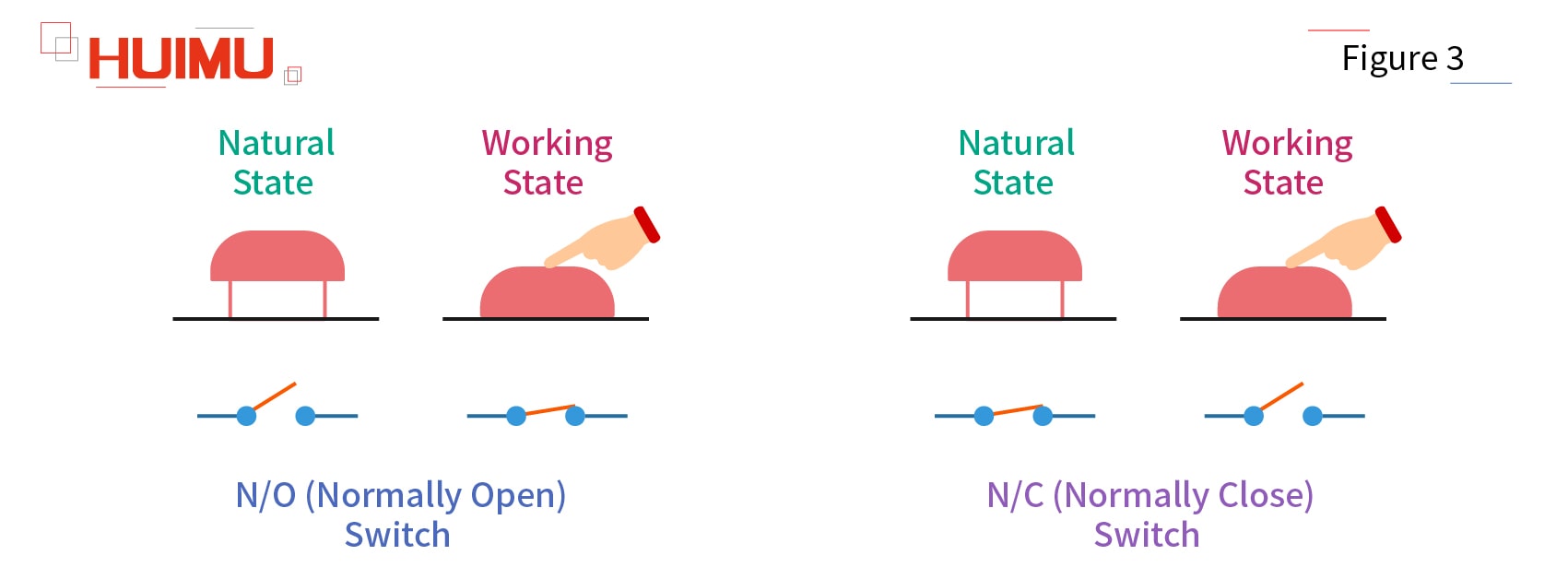
NO (Normally Open): If the throw circuit is disconnected to the pole by default (when the pole is not subject to any external forces), this throw circuit will be called the normally open circuit (NO circuit, N/O circuit), and the switch will be called normally open switch (NO switch, N/O switch).
NC (Normally Close): If the throw circuit is connected to the pole by default (when the pole is not subject to any external forces), this throw circuit will be called the normally closed circuit (NC circuit, N/C circuit), and the switch will be called normally closed switch (NC switch, N/C switch).
SPDT switch is a five terminal switch device — two input terminals, and three output terminals (two terminals connect to the load, and one terminal connect to the common terminal). And if one of SPDT switch output terminals does not connect to any circuit (which means only one control circuit and one output circuit are connected to the SPDT switch), the SPDT switch functions as a SPST switch.
Generally, the SPDT switch will be more suitable and efficient for some special applications than what two normal SPST switches (which need two control circuits) can do, like switching two different power supplies in opposite status, or activating two circuits with different functions in opposite status.
1.2 How does SPDT Switch work
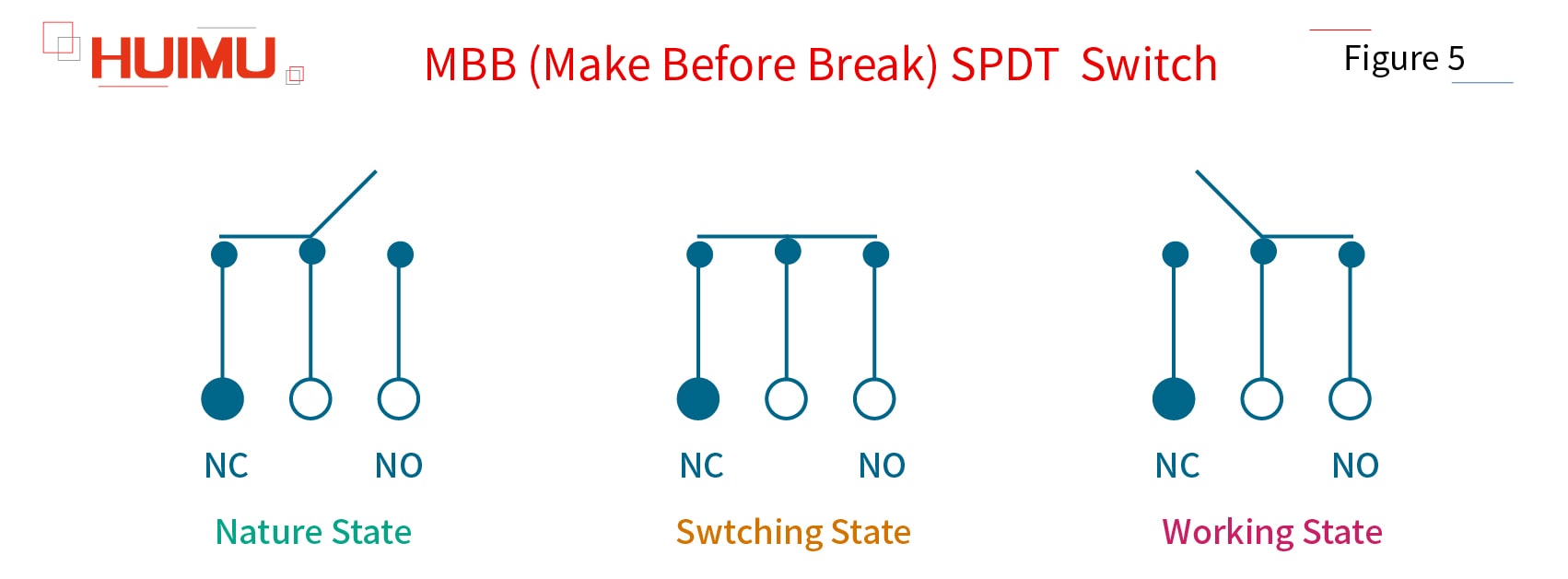
According to the way of operating, the single pole double throw switch can be divided into BBM type SPDT switch (break-before-make) and MBB type SPDT switch (make-before-break).
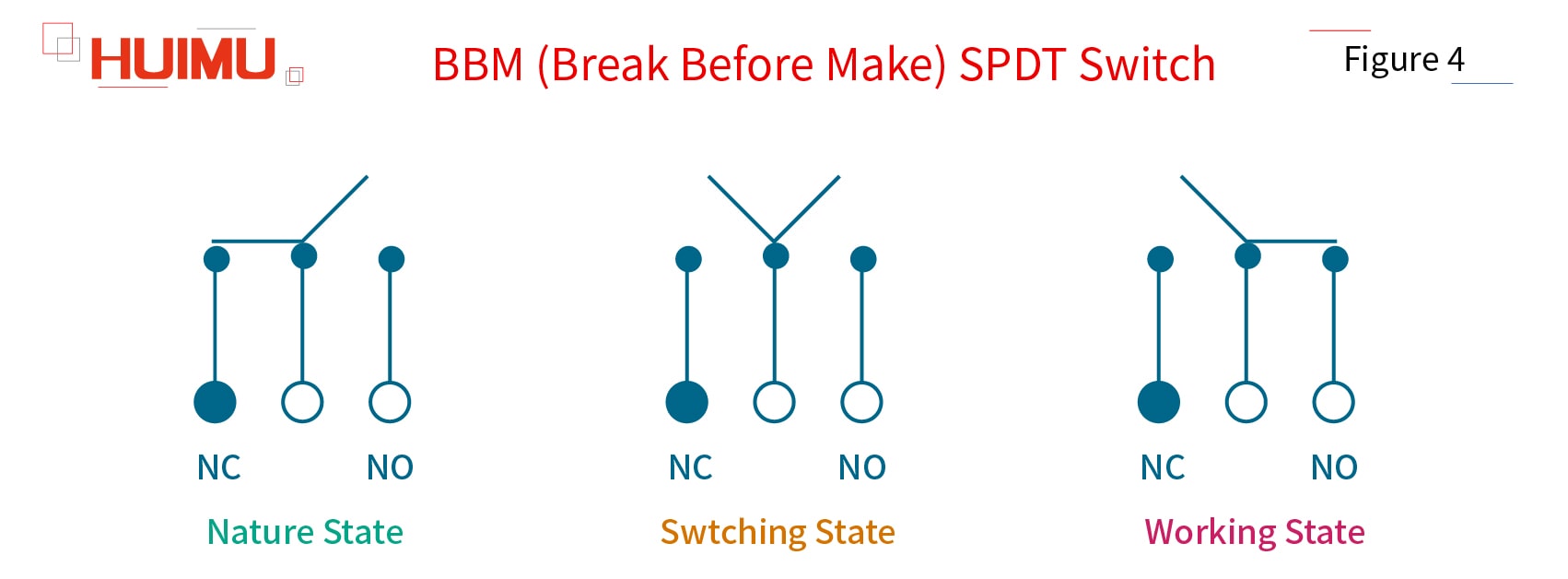
1) BBM (Break Before Make) SPDT Switch
By default, the pole of the BBM SPDT switch is connected to NC throw circuit and disconnected from the NO throw circuit. When the break-before-make switch is switched, it will first disconnect to the NC circuit, and then connect to the NO circuit.
2) MBB (Make Before Break) SPDT Switch
By default, the pole of the MBB SPDT switch is connected to NC throw circuit and disconnected from the NO throw circuit. When the make-before-break switch is switched, it will first connect to the NO circuit, and then disconnect to the NC circuit.