In computer engineering, logic circuit or logic family may refer to one of two related concepts. A logic family of monolithic digital integrated circuit devices is a group of electronic logic gates constructed using one of several different designs, usually with compatible logic levels and power supply characteristics within a family. Many logic families were produced as individual components, each containing one or a few related basic logical functions, which could be used as "building-blocks" to create systems or as so-called "glue" to interconnect more complex integrated circuits.
The list of packaged building-block logic families can be divided into categories, listed here in roughly chronological order of introduction, along with their usual abbreviations:
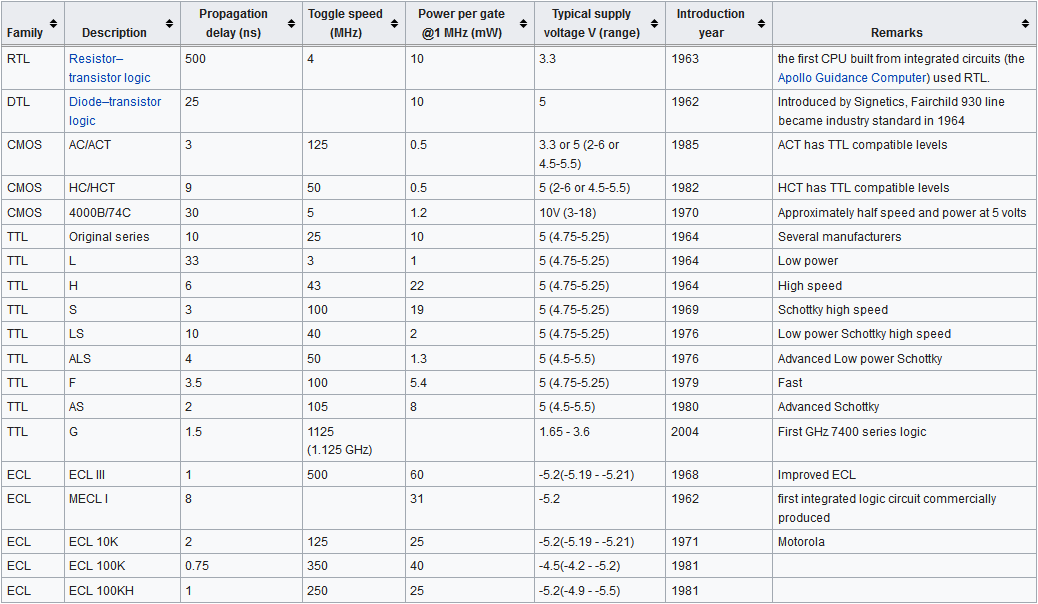
The list of packaged building-block logic families can be divided into categories, listed here in roughly chronological order of introduction, along with their usual abbreviations:
1. Resistor–transistor logic (RTL)
1.1 Direct-coupled transistor logic (DCTL)
1.2 Resistor–capacitor–transistor logic (RCTL)
1.1 Direct-coupled transistor logic (DCTL)
1.2 Resistor–capacitor–transistor logic (RCTL)
2. Diode–transistor logic (DTL)
2.1 Complemented transistor diode logic (CTDL)
2.2 High-threshold logic (HTL)
2.1 Complemented transistor diode logic (CTDL)
2.2 High-threshold logic (HTL)
3. Emitter-coupled logic (ECL)
3.1 Positive emitter-coupled logic (PECL)
3.2 Low-voltage positive emitter-coupled logic (LVPECL)
3.3 Complementary transistor micrologic (CTuL)
3.1 Positive emitter-coupled logic (PECL)
3.2 Low-voltage positive emitter-coupled logic (LVPECL)
3.3 Complementary transistor micrologic (CTuL)
4. Gunning transceiver logic (GTL)
6. P-type metal–oxide–semiconductor logic (PMOS)
7. N-type metal–oxide–semiconductor logic (NMOS)
7.1 Depletion-load NMOS logic
7.2 High-density nMOS (HMOS)
7.1 Depletion-load NMOS logic
7.2 High-density nMOS (HMOS)
10. Integrated injection logic (I2L)


 Contact Wear is the
Contact Wear is the 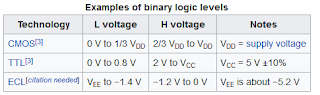
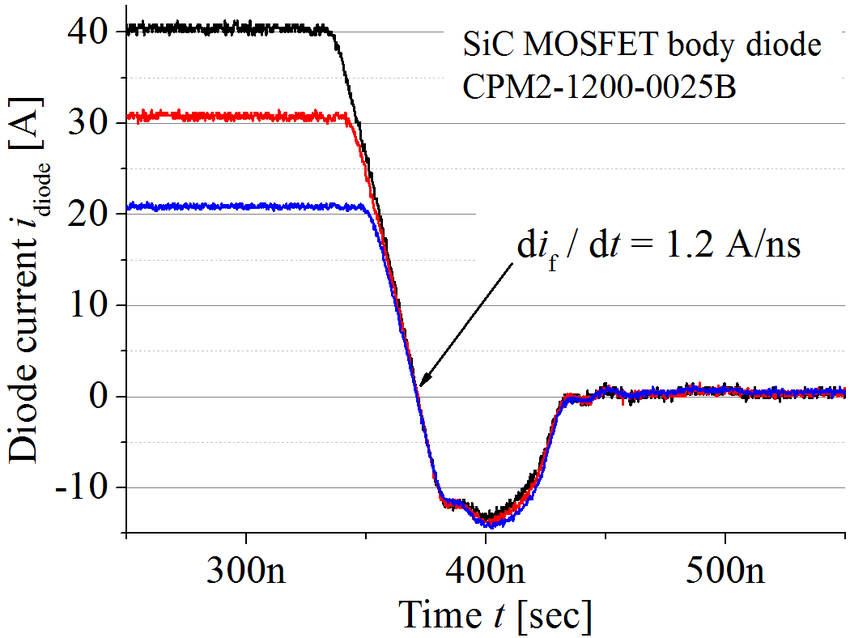 Switching speed or switching rate, is the switching frequency of the
Switching speed or switching rate, is the switching frequency of the 
 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is the branch of electrical engineering concerned with the unintentional generation, propagation and reception of electromagnetic energy which may cause unwanted effects such as
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is the branch of electrical engineering concerned with the unintentional generation, propagation and reception of electromagnetic energy which may cause unwanted effects such as 