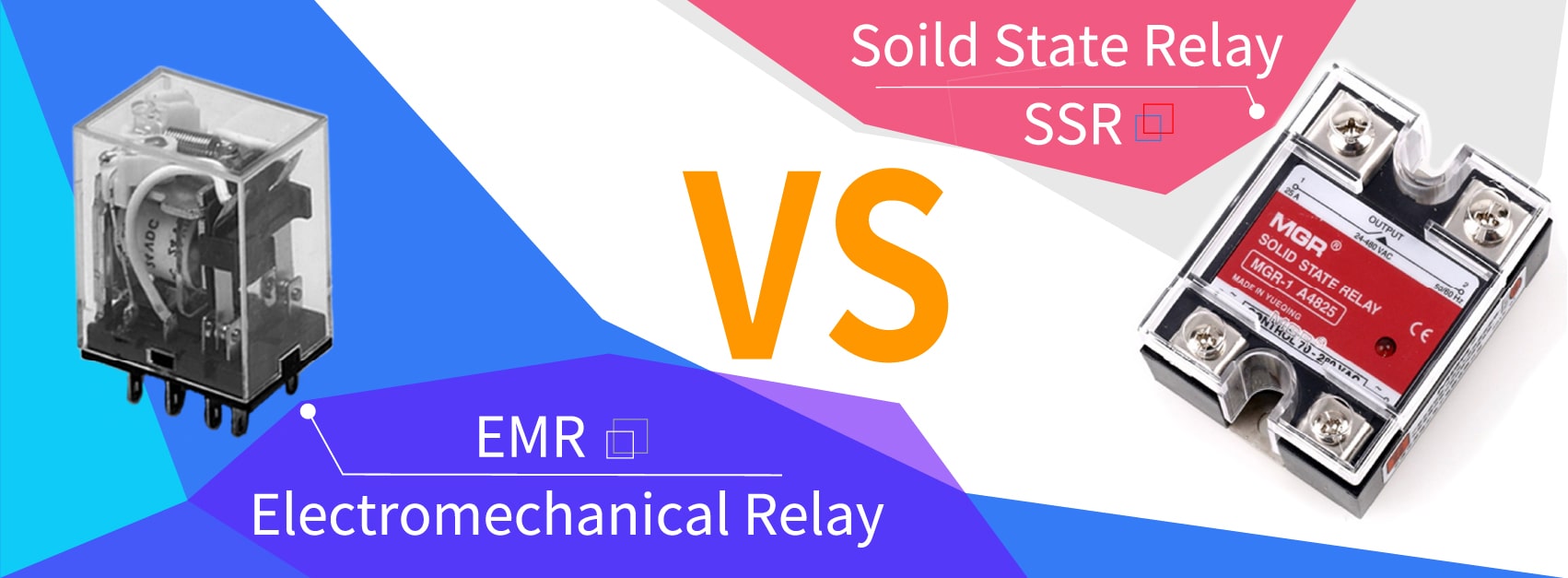
§1. What is a Solid State Relay (SSR)

Solid State Relay (also known as SSR, SS Relay, SSR relay or SSR switch, solid-state contactor, power electronic switch, automotive relays, electronic power relays, and electrical signal contactors) is an integrated contactless electronic switch device that is compactly assembled from an integrated circuit (IC) and discrete components. Depending on the switching characteristics of the electronic components (such as switching transistors, bi-directional thyristors and other semiconductor components), the SSRs are able to switch the "ON" and "OFF" state of the load very quickly through the electronic circuit, just like the function of traditional mechanical relays. Compared with the previous "coil-reed contact" relay, namely Electromechanical Relay(EMR), there is no movable mechanical part inside the SSR, and there is also no mechanical action during the switching process of the SSR. Therefore, the Solid-State Relay is also called "non-contact switch".
The structural characteristics of the SSR switch make it superior to the EMR. The main advantages of solid state relays are as follows:
● The semiconductor component acts as a switch for the relay, which is small in size (compact size) and long in life (long lifetime).
● Better Electro-Magnetic Compatibility than EMR - immunity to Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) and Electro-Magnetic Interference (EMI), low electromagnetic interference, and low electromagnetic radiation.
● No moving parts, no mechanical wear, no action noise, no mechanical failure, and high reliability.
● No spark, no arc, no burning, no contact bounce, and no wear between contacts.
● With "zero voltage switching, zero current shutdown" function, easy to achieve "zero voltage" switching.
● Fast switching speed (SSR switching speed is 100 times higher than general EMR), high operating frequency.
● High sensitivity, low electrical level control signals (SSR can directly drive large current loads through the small current control signals), compatible with logic circuit (TTL, CMOS, DTL, HTL circuits), easy to implement multiple functions.
● Generally packaged by insulation material, with good moisture resistance, mildew resistance, corrosion resistance, vibration resistance, mechanical shock resistance and explosion-proof performance.
Furthermore, the amplification and drive function of the solid-state relay is very suitable for driving high-power actuator, which is more reliable than electromagnetic relays (EMR). The control switches of solid state relays require very low power, so the low control currents can be used to control high load currents. And, the solid-state relay uses mature and reliable optoelectronic isolation technology between the input and output terminals. This technology allows the output signal of the low power device to be directly connected to the input control terminals of the solid state relay, to control the high power device at the output terminal of the solid-state relay without the need for additional protection circuitry to protect the weak current device, because the "small control current device" (connected to the SSR input terminal) and the "large control power supplies" (connected to the SSR output terminal) have been electrically isolated. Besides, AC solid state relays use the "zero-crossing detector" technology to safely apply the AC-SSR to the computer's output interface without causing a series of interferences or even serious failures to the computer. And these features cannot be implemented by EMR.
Because of the inherent characteristics of solid state relays and the above advantages, SSR has been widely used in various fields since it came out in 1974, and has completely replaced electromagnetic relays in many fields where electromagnetic relays cannot apply. Especially in the computer automatic control system field, because the solid state relay requires very low drive power and are compatible with the logic circuit, and can also directly drive the output circuit without the need for an additional intermediate digital buffer.

At present, solid state relays perform well in military, chemical, industrial automation control devices, electro mobile, telecommunication, civil electronic control equipment, as well as security and instrumentation applications, such as electric furnace heating system, computer numerical control machine (CNC machine), remote control machinery, solenoid valve, medical equipment, lighting control system (such as traffic light, scintillator, stage lighting control system), home appliances(such as washing machine, electric stove, oven, refrigerator, air conditioner), office equipment (such as photocopier,printers, fax machines and Multi-function printers), fire safety systems, electric vehicle charging system and so on. All in all, solid state relays can be used in any application requiring high stability (optical isolation, high immunity), high performance (high switching speed, high load current), and small package size.
Of course, solid state relays also have some disadvantages, including: exist on-state voltage drop and output leakage current, need heat dissipation measures, higher purchase cost than EMR, DC relays and AC relays are not universal, single control state, small number of contact groups, and poor overload capability. While some special customized solid state relays can solve some of the above problems, these disadvantages need to be considered and optimized when designing circuits and applying SSRs to maximize the benefits of solid state relays.

Solid State Relay (also known as SSR, SS Relay, SSR relay or SSR switch, solid-state contactor, power electronic switch, automotive relays, electronic power relays, and electrical signal contactors) is an integrated contactless electronic switch device that is compactly assembled from an integrated circuit (IC) and discrete components. Depending on the switching characteristics of the electronic components (such as switching transistors, bi-directional thyristors and other semiconductor components), the SSRs are able to switch the "ON" and "OFF" state of the load very quickly through the electronic circuit, just like the function of traditional mechanical relays. Compared with the previous "coil-reed contact" relay, namely Electromechanical Relay(EMR), there is no movable mechanical part inside the SSR, and there is also no mechanical action during the switching process of the SSR. Therefore, the Solid-State Relay is also called "non-contact switch".
The structural characteristics of the SSR switch make it superior to the EMR. The main advantages of solid state relays are as follows:
● The semiconductor component acts as a switch for the relay, which is small in size (compact size) and long in life (long lifetime).
● Better Electro-Magnetic Compatibility than EMR - immunity to Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) and Electro-Magnetic Interference (EMI), low electromagnetic interference, and low electromagnetic radiation.
● No moving parts, no mechanical wear, no action noise, no mechanical failure, and high reliability.
● No spark, no arc, no burning, no contact bounce, and no wear between contacts.
● With "zero voltage switching, zero current shutdown" function, easy to achieve "zero voltage" switching.
● Fast switching speed (SSR switching speed is 100 times higher than general EMR), high operating frequency.
● High sensitivity, low electrical level control signals (SSR can directly drive large current loads through the small current control signals), compatible with logic circuit (TTL, CMOS, DTL, HTL circuits), easy to implement multiple functions.
● Generally packaged by insulation material, with good moisture resistance, mildew resistance, corrosion resistance, vibration resistance, mechanical shock resistance and explosion-proof performance.
Furthermore, the amplification and drive function of the solid-state relay is very suitable for driving high-power actuator, which is more reliable than electromagnetic relays (EMR). The control switches of solid state relays require very low power, so the low control currents can be used to control high load currents. And, the solid-state relay uses mature and reliable optoelectronic isolation technology between the input and output terminals. This technology allows the output signal of the low power device to be directly connected to the input control terminals of the solid state relay, to control the high power device at the output terminal of the solid-state relay without the need for additional protection circuitry to protect the weak current device, because the "small control current device" (connected to the SSR input terminal) and the "large control power supplies" (connected to the SSR output terminal) have been electrically isolated. Besides, AC solid state relays use the "zero-crossing detector" technology to safely apply the AC-SSR to the computer's output interface without causing a series of interferences or even serious failures to the computer. And these features cannot be implemented by EMR.
Because of the inherent characteristics of solid state relays and the above advantages, SSR has been widely used in various fields since it came out in 1974, and has completely replaced electromagnetic relays in many fields where electromagnetic relays cannot apply. Especially in the computer automatic control system field, because the solid state relay requires very low drive power and are compatible with the logic circuit, and can also directly drive the output circuit without the need for an additional intermediate digital buffer.

At present, solid state relays perform well in military, chemical, industrial automation control devices, electro mobile, telecommunication, civil electronic control equipment, as well as security and instrumentation applications, such as electric furnace heating system, computer numerical control machine (CNC machine), remote control machinery, solenoid valve, medical equipment, lighting control system (such as traffic light, scintillator, stage lighting control system), home appliances(such as washing machine, electric stove, oven, refrigerator, air conditioner), office equipment (such as photocopier,printers, fax machines and Multi-function printers), fire safety systems, electric vehicle charging system and so on. All in all, solid state relays can be used in any application requiring high stability (optical isolation, high immunity), high performance (high switching speed, high load current), and small package size.
Of course, solid state relays also have some disadvantages, including: exist on-state voltage drop and output leakage current, need heat dissipation measures, higher purchase cost than EMR, DC relays and AC relays are not universal, single control state, small number of contact groups, and poor overload capability. While some special customized solid state relays can solve some of the above problems, these disadvantages need to be considered and optimized when designing circuits and applying SSRs to maximize the benefits of solid state relays.