1. What is silicone gel?

Silicone gel is widely used in electronic components (such as precision electronic components, solid state relays, back-lights, solar energy, connectors, electrical modules, discrete devices, integrated circuit boards, etc.). Silicone gel is applied, poured or potted on electronic components to provide protection against water, moisture, gas contamination and shock absorption. Silicone gel is completely transparent when not doped with other materials, so potted electronic components can be seen directly. Even if the silicone gel is damaged, it can be repaired by re-potting, so the faulty components can be easily detected and replaced.
For the convenience of storage and use, the silicone gel is divided into two groups of liquid raw materials (A and B) before curing, just like AB glue. After fully mixing in a certain proportion, under the catalysis of the metal platinum complexes, the vinyl group on the silicone gel undergoes an addition reaction with the silicon hydrogen group on the cross-linking agent molecule, so that the silicone gel is easy to achieve a high degree of vulcanization. Finally, the liquid silicone gel gradually becomes a thick semi-solid elastomer. The whole reaction process does not produce by-products, so the gel body does not shrink during vulcanization.
The properties of silicone gel can be summarized as follows:
- It has stable physical and chemical properties, and can be used in a wide temperature range (-60 ℃ ~ 200 ℃);
- It has good electrical properties and weather resistance, and can be used in harsh environments such as high voltage, high temperature, and sunlight;
- It has good fluidity before curing, and can be injected into the subtleties of integrated circuit micro-components, which can effectively isolate electronic products from the external environment;
- It has a certain viscosity, and can be bonded to most materials without adding any adhesive agent or spraying adhesive on the bonding surface before curing;
- It does not contain solid fillers and is completely transparent. When it is used as a potting material, it is convenient to observe the internal structure of the potted component;
- It has good self-repair ability, and can meet the replacement of potted components and the circuit detection of metal probes;
- The gel body has good toughness and shock absorption effect after curing.
2. How do we use silicone gel?
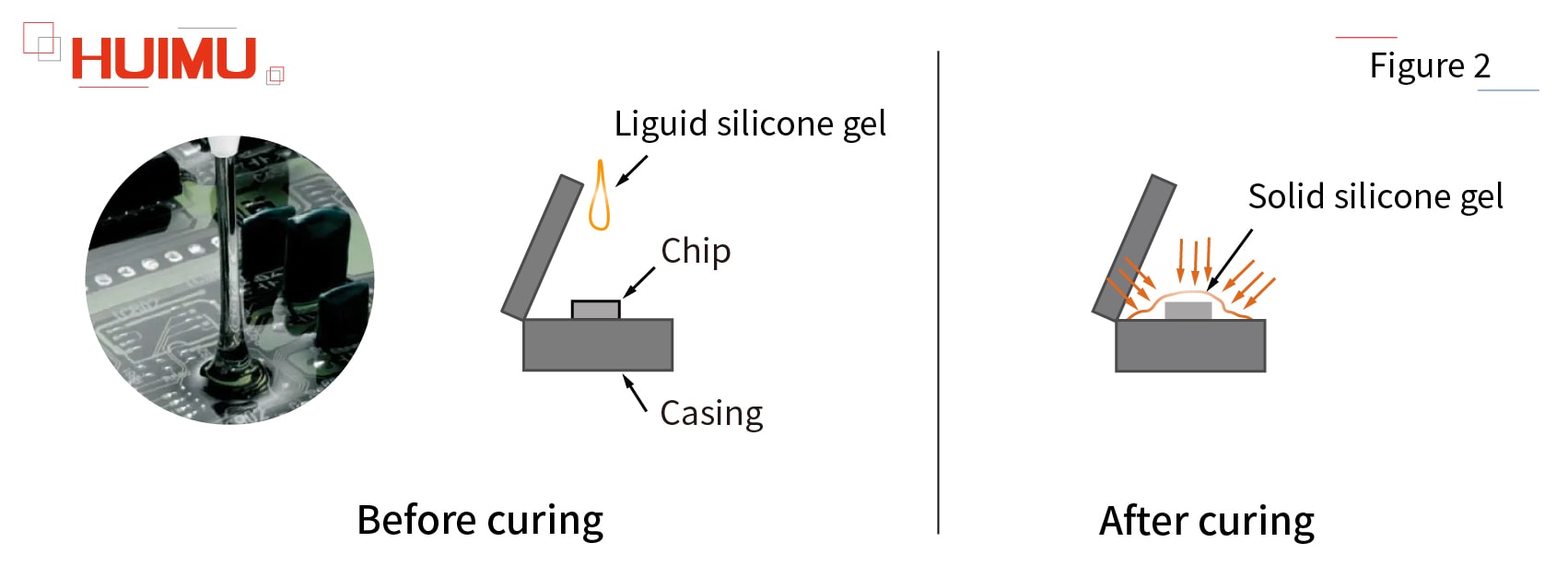
Our supplier will provide us with raw material A and raw material B of liquid silicone gel. As long as they are mixed in a ratio of 1:1, they can be solidified into solid silicone gel after 12 hours at room temperature. Before curing, silicone gel is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic viscous liquid, we will put it to the top of the solid state relay chip during the manufacturing process. After curing, the silicone gel becomes a jelly-like elastic substance. Silicone gel has excellent insulation, ductility and thermal properties, so it can effectively protect the chip from high temperature, shock and other damage, greatly improving the service life and performance stability of the solid state relay.
3. How do we clean up silicone gel?
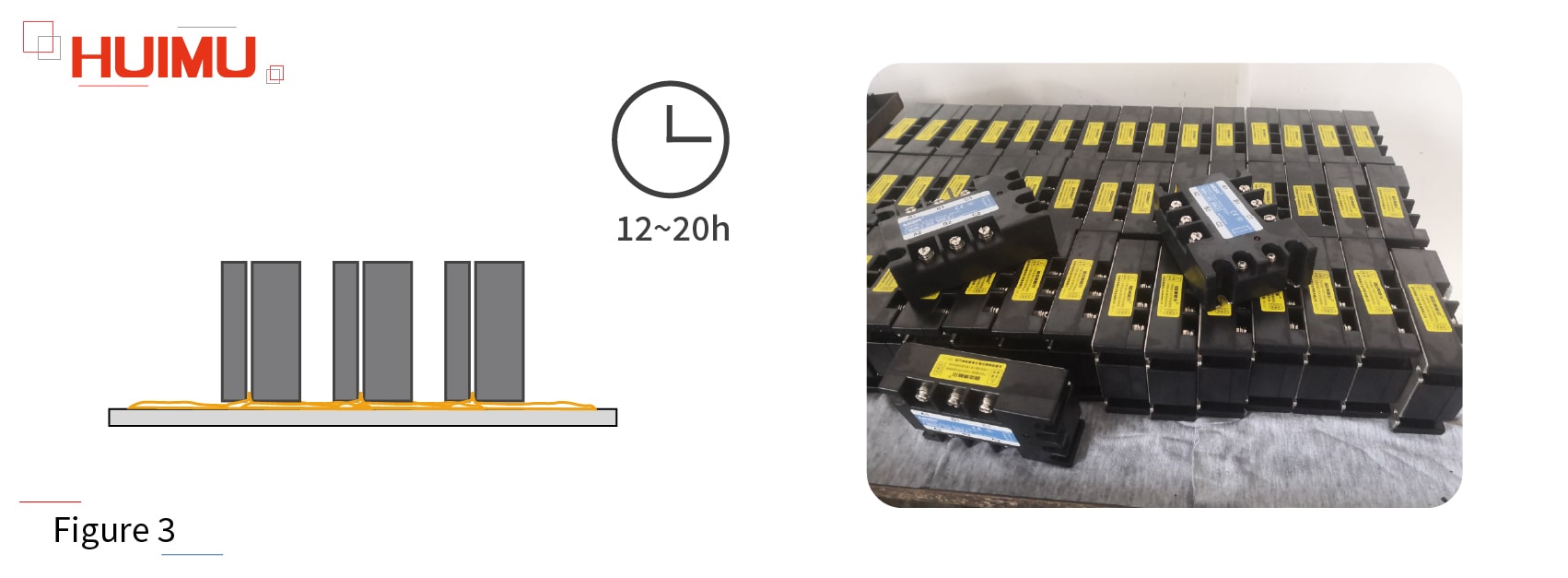
The curing time of silicone gel is about 12~20 hours (the lower the temperature, the longer the time). If the temperature is too low or the ratio is incorrect, a little part of the liquid silicone gel will remain inside the solid state relay. Usually we put the solid state relay on its side to let the excess raw material and uncured liquid silicone gel flow out. Then we wipe it out, and package the solid state relay.
4. Precautions
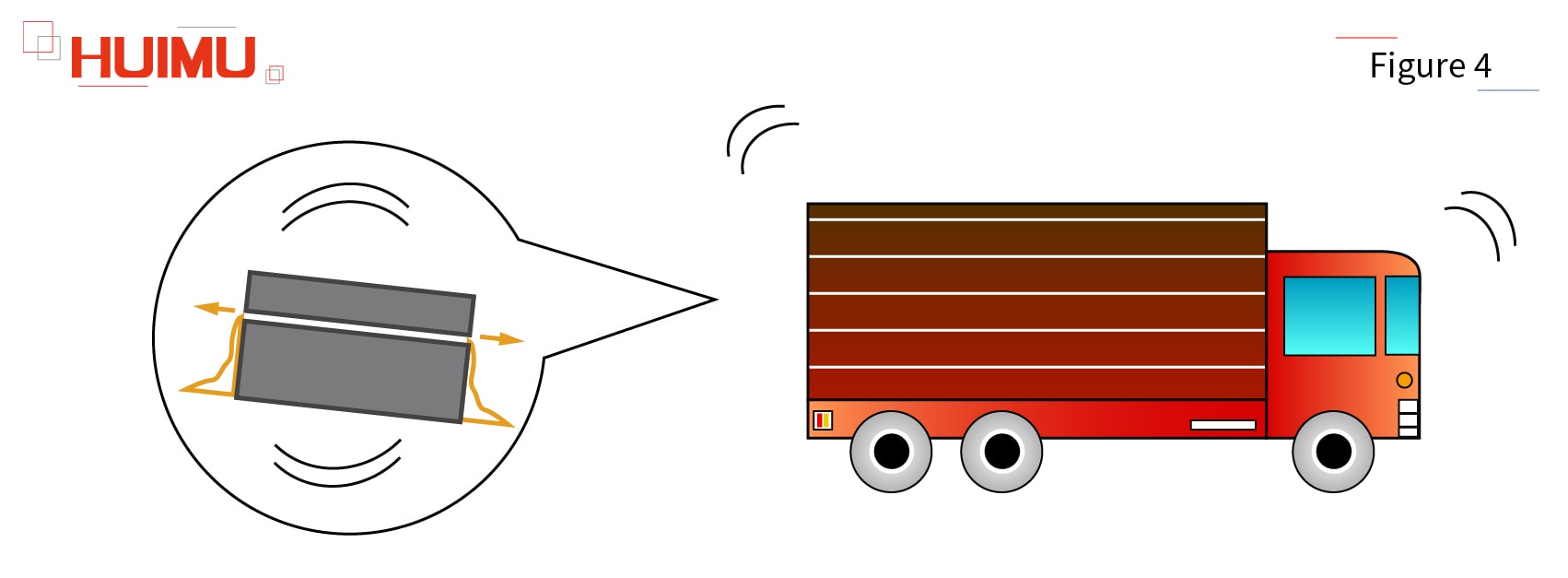
It should be noted that if the solid-state relay is not standing on its side long enough, or a very small part of the silicone gel is not cured, then due to the vibration during transportation, the liquid silicone gel will flow out from the gap of the solid-state relay shell, thereby contaminated the appearance of the solid-state relay.
*If the paper packaging or plastic packaging of the solid state relay is found to be damaged and corroded by liquid when receiving the goods, it is very likely that the rain/sea water corrosion is caused by the fault of the freight company during transportation. So you need to file a claim with the freight company.
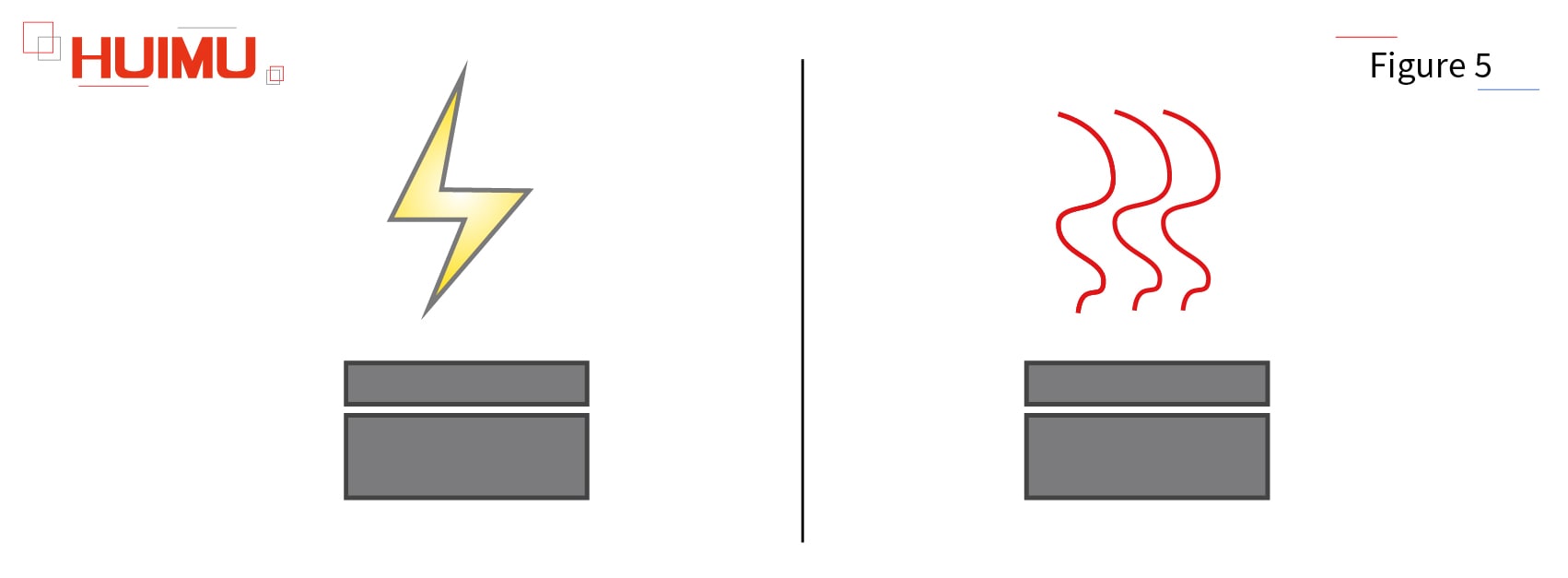
Each solid state relay will undergo high voltage withstand test and high temperature aging test before leaving the factory, and the unqualified solid state relay will be discarded. Since silicone gel is a high voltage resistant, heat-insulating, and non-flammable material, it will not have any impact on the performance and safety of solid-state relays. So if you find liquid silicone gel on the surface of the solid state relay, just wipe it.
